Smart contracts are great, but… only developers can read and write them!
Imagine a world where contracts don’t just automate transactions for the tech-savvy but also adapt, enforce, and interact in real time without costly delays, lawyers, or accountants.
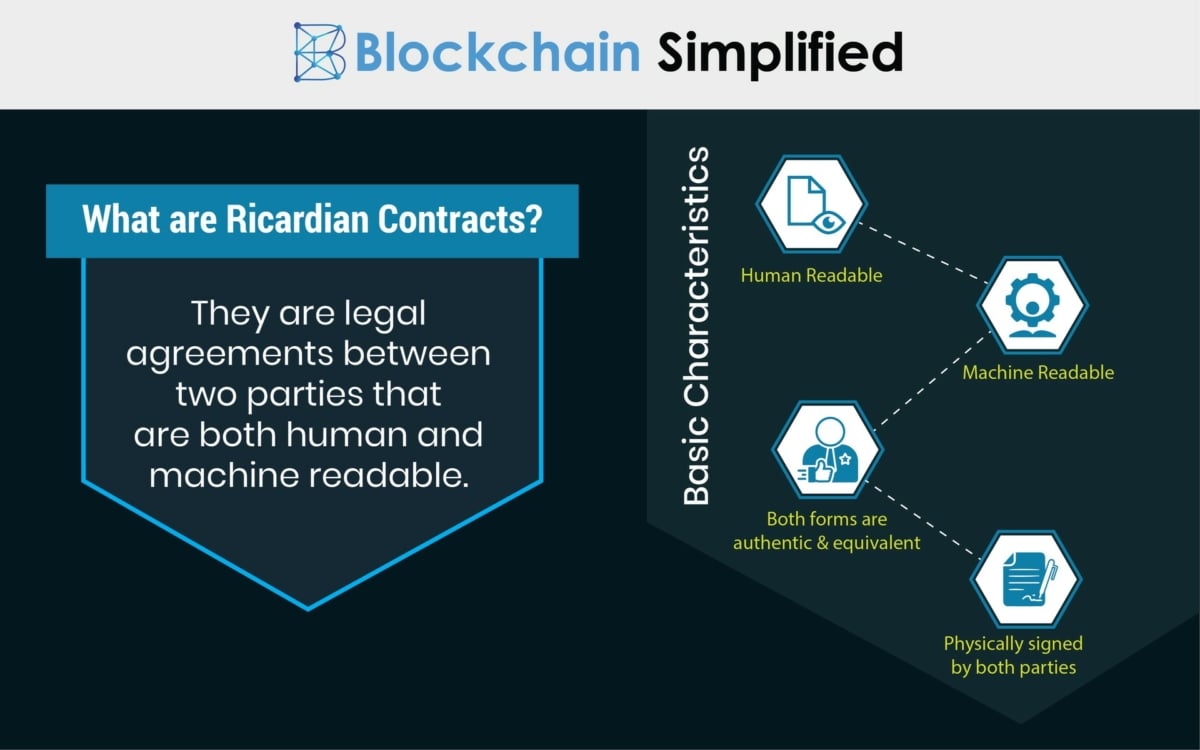
AI-powered “Ricardian smart contracts” will bring us closer to this future.
While traditional smart contracts require coding skills to create and understand, Ricardian smart contracts combine plain language with blockchain-executable code, bridging legal agreements and digital technology.
Add AI to this mix, and you get contracts that are responsive, accessible, and able to handle real-world events.
There’s just one problem. The technology doesn’t exist yet.
Like a disassembled motor, the parts are there, but no one has put them together yet.
Someone will.
And whoever that is will not only provide humanity with a great service. But also get rich–like really rich–in the process.
The Problem with Traditional Smart Contracts
The promise of smart contracts lies in automating agreements, eliminating middlemen, and reducing human error. However, most smart contracts require programming expertise, making them largely inaccessible for the average person.
Even for those with coding skills, legal expertise is often required to ensure compliance and enforceability, which adds both cost and complexity.
Enter AI-enhanced Ricardian smart contracts, which allow everyday users to interact with legally binding, self-enforcing agreements without lawyers, accountants, or specialized developers.
Ricardian smart contracts combine traditional legal language with blockchain-ready code, but integrating AI makes them even more powerful.
Imagine drafting a contract just by explaining terms in natural language.
AI can take your conversational input and translate it into a legally sound agreement that is both human and machine readable.
This opens up smart contracts for freelancers, small businesses, and individuals, who can now easily and affordably access the power of automation and trust.
Making Contracts Accessible for All
Imagine a freelance designer needing a contract for a new project.
Instead of hiring a lawyer, they could describe their expectations, deadlines, and payment terms, and an AI would translate this conversation into a legally binding contract, enforceable on the blockchain.
This process eliminates the need for contract lawyers or developers to set up or enforce agreements, and triggers instant payment on contract fulfillment in a way that is accessible for everyone.
AI Ricardian contracts effectively put power in the hands of individuals, reducing the cost and complexity of legal agreements.
Real-Time Interactions with the Real World
AI-enhanced Ricardian smart contracts don’t just store conditions—they monitor and react to real-world events, allowing terms to be modified or fulfilled as they happen.
In construction, for example, a builder might give a quote based on today’s material costs. With an AI-powered Ricardian smart contract, the price adjusts automatically if material costs change by the day of purchase, avoiding disputes over extra charges and eliminating accounting delays.
IoT integrations make this system even more responsive.
Once materials arrive on-site, an RFID tag can signal the contract to trigger payments to suppliers automatically, removing the invoicing and paperwork that traditionally require accountant oversight.
By responding in real time, Ricardian smart contracts reduce delays, save on administrative costs, and create a more transparent process from end to end.
In simpler transactions, such as online retail, a Ricardian smart contract could handle returns.
Imagine buying a product that arrives damaged. Instead of filing a return claim and waiting for approval, an AI-enhanced contract could trigger an automatic refund as soon as the returned item is shipped.
This makes transactions faster and more seamless for buyers and sellers alike.
AI-Driven Verification for Enhanced Fairness and Flexibility
Another major benefit of AI-enhanced Ricardian smart contracts is their ability to verify fulfillment before issuing payments.
Let’s say a short-term rental agreement is in place.
After the rental period ends, the AI checks with both the renter and host to confirm they’re satisfied before releasing final payments or deposits. This extra layer of verification keeps all parties accountable without needing a third party to mediate, reducing the need for legal intervention.
In situations where terms are met, the AI remits payment in whatever cryptocurrency was agreed upon, ensuring quick and accurate transactions.
This feedback-driven process ensures that both parties’ satisfaction is prioritized, bringing a level of fairness and flexibility that static contracts lack. With these features, Ricardian smart contracts make everyday transactions smoother while avoiding the need for lawyers or dispute resolution professionals.
Predictive Contract Management and Adaptive Adjustments
AI adds predictive capabilities to Ricardian smart contracts, allowing them to detect potential issues before they arise.
In a global supply chain, for instance, AI could track stock levels, shipping schedules, and even weather conditions to foresee potential disruptions. By predicting and adjusting to these variables, the contract could modify delivery dates or adjust payment schedules without the need for external accountants or administrative involvement.
Consider a large shipment delayed due to port congestion.
The AI-enhanced Ricardian contract detects the delay, notifies all parties, and adjusts terms as needed—preventing costly disruptions and avoiding contract breaches. The result is a self-managing contract that keeps operations smooth, avoiding the manual oversight and frequent adjustments that would otherwise demand professional input.
When Adaptability Isn’t Necessary: The Case for Static Contracts
While adaptability is a game-changer in many contracts, not all agreements benefit from flexibility. Some need to stay fixed to ensure reliability and consistency.
Wills and trusts, for example, must remain immutable to uphold a person’s final wishes. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) protect sensitive information indefinitely, requiring permanent terms to ensure confidentiality. Similarly, loan and mortgage agreements rely on stable repayment schedules and interest rates, providing the predictability both parties need.
In cases like these, Ricardian smart contracts can still provide transparency and enforceability without requiring adaptability.
By balancing flexible options for dynamic contracts with fixed options for agreements requiring stability, Ricardian smart contracts ensure both the power of automation and the certainty of traditional legal protections.
Challenges of AI-Enhanced Ricardian Smart Contracts
While AI-enhanced Ricardian smart contracts bring undeniable benefits, they come with some challenges.
Transparency is crucial:
AI-driven decisions need to be clear and interpretable, especially in legal contexts where accountability is essential. AI can also introduce biases that affect contract outcomes, making oversight necessary to ensure fairness for all parties.
Additionally, legal recognition of AI-enhanced Ricardian smart contracts is essential for broad adoption.
Courts and regulators will need to accept AI-driven decisions as enforceable and implement clear frameworks that support the use of AI-powered contracts across different industries.
Addressing these issues will be crucial to the widespread use and acceptance of Ricardian smart contracts in both corporate and personal transactions.
The Future of Smart Contracts – Making Web3 Practical for All
AI-enhanced Ricardian smart contracts offer an unprecedented opportunity to democratize access to reliable, adaptable agreements.
By eliminating the need for extensive legal and accounting fees, these contracts could transform everyday transactions, from simple purchases to complex projects.
They promise a future where contracts are responsive, accessible, and practical, removing the barriers that keep smart contracts out of reach for most people.
By making contracts interactive and adaptable, they allow us to buy, build, and interact with greater efficiency and security. And best of all—no coding or legal expertise required!